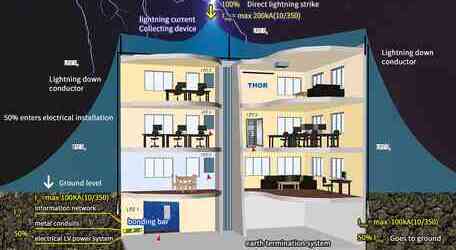
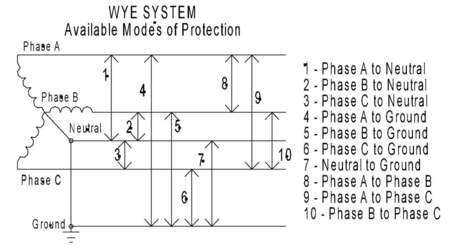
Problems of electrical coordination between SPD and surge backup protector

With varistor as the core non-linear component SPD, during normal use, the leakage current of the varistor is increased from microampere to milliampere due to the influence of power supply voltage fluctuation or varistor aging, and varistor appears The temperature of the resistor body rises, and the leakage current continues to rise, until the SPD plastic shell is deformed by heat and is destroyed by fire.
The failure mode of SPD with varistor as the core non-linear component is:
Leakage current rises → SPD temperature rises → Leakage current continues to rise → SPD temperature continues to rise → SPD fails → SPD burns.
The national standard GB 18802.1-2011 Low Voltage Surge Protector (SPD) Part 1: Protector performance requirements and test methods for low-voltage power distribution systems stipulate that SPD non-metallic parts must be made of flame-retardant materials and have a certain heat resistance capability. Withstand the thermal stability test required by relevant.
At the same time, the non-linear component SPD with varistor as the core must be equipped with a release device with thermal protection, leakage current protection and overcurrent protection. The minimum operating current of the separation device is 2 mA (the DC operating voltage value of the varistor) Defined as the voltage across the varistor under a current of 1 mA). In the test, the SPD can operate when the minimum leakage current of 2 mA occurs, and cut off the voltage applied to the varistor. At the same time, there is no obvious appearance of the SPD damage. Therefore, with the varistor as the core non-linear element SPD, when the varistor has a leakage current of 2 mA, the disconnector can act to remove the fault SPD, ensuring the safe operation of the overall power supply line.
A surge backup protector with a rated lightning current of 20 kA and a power frequency operating current of 3 A is used in series with the SPD. When the leakage current of the SPD reaches 2 mA, the built-in disconnector will operate to protect the SPD from the power supply. Voltage, the leakage current of 2 mA is only 0.007 times the operating current of the backup protector, which is far less than the power frequency operating current of the surge backup protector. Therefore, when the SPD has a leakage current of 3 amperes, the SPD will burn out long ago.
Conclusion:
1. For SPDs with built-in disconnectors, generally speaking, surge backup protectors are not required to protect SPDs. Only surge backup protectors can be used to protect the power distribution network from breakage of other components in the SPD circuit. The harm.
2. For SPDs that do not have a built-in disconnector, an external temperature protection type circuit breaker can be used to protect the SPD.
When the power frequency operating current of the surge backup protector is less than 2 mA, it can be used in series with the SPD.