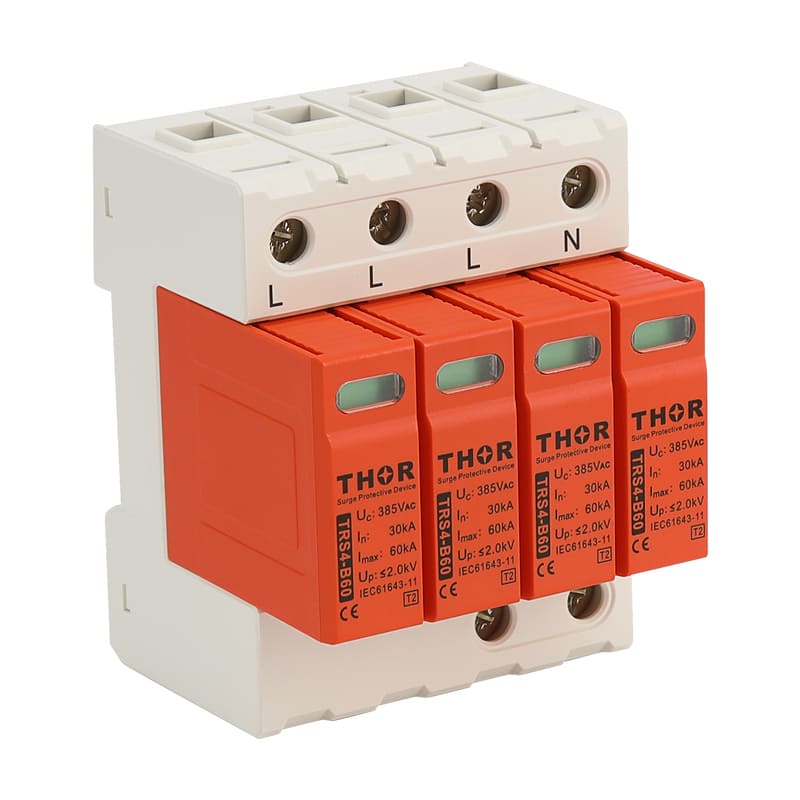
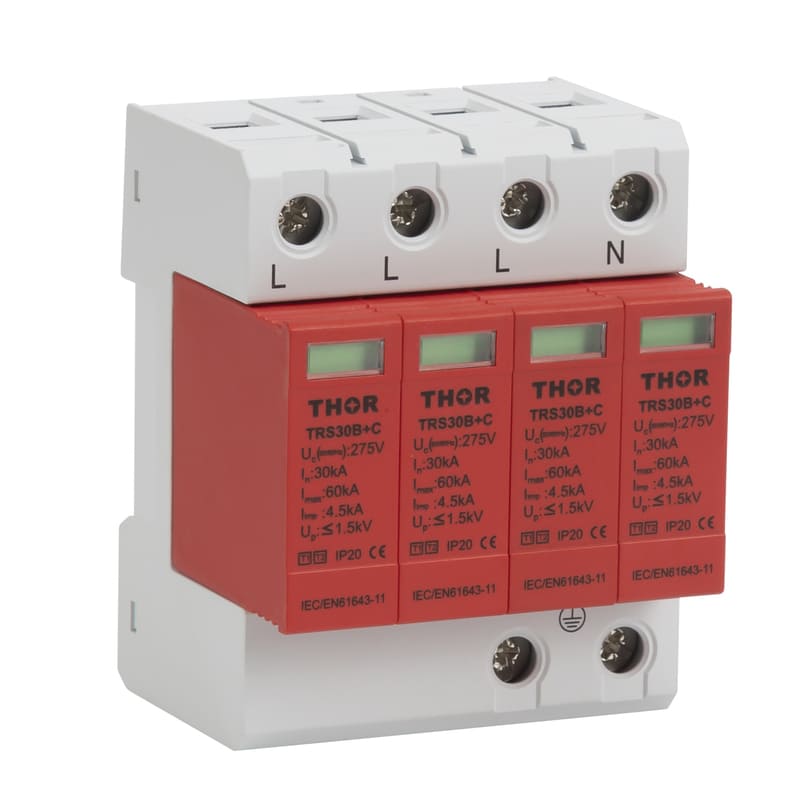
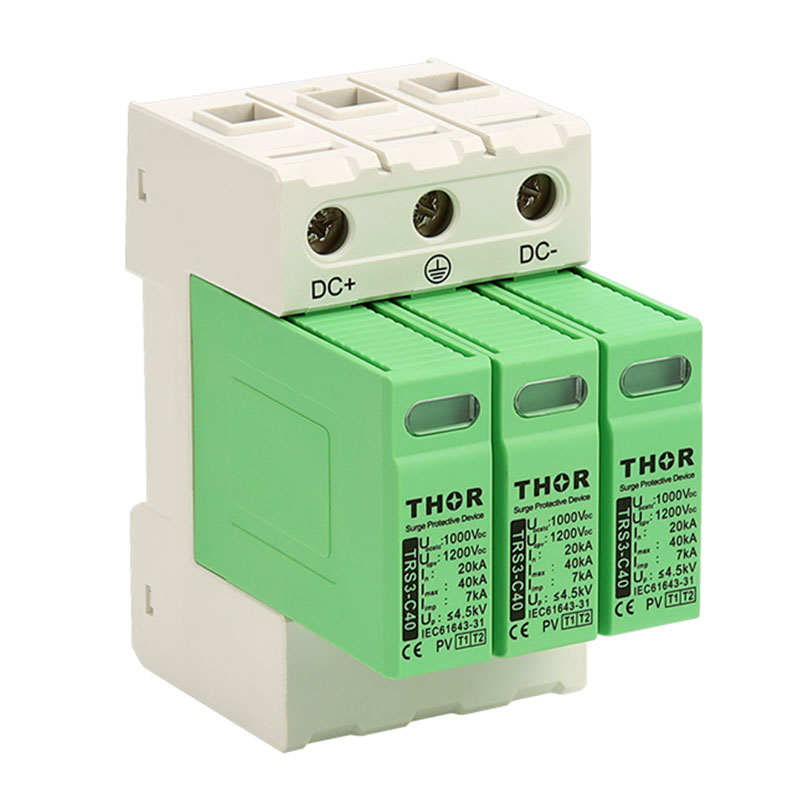
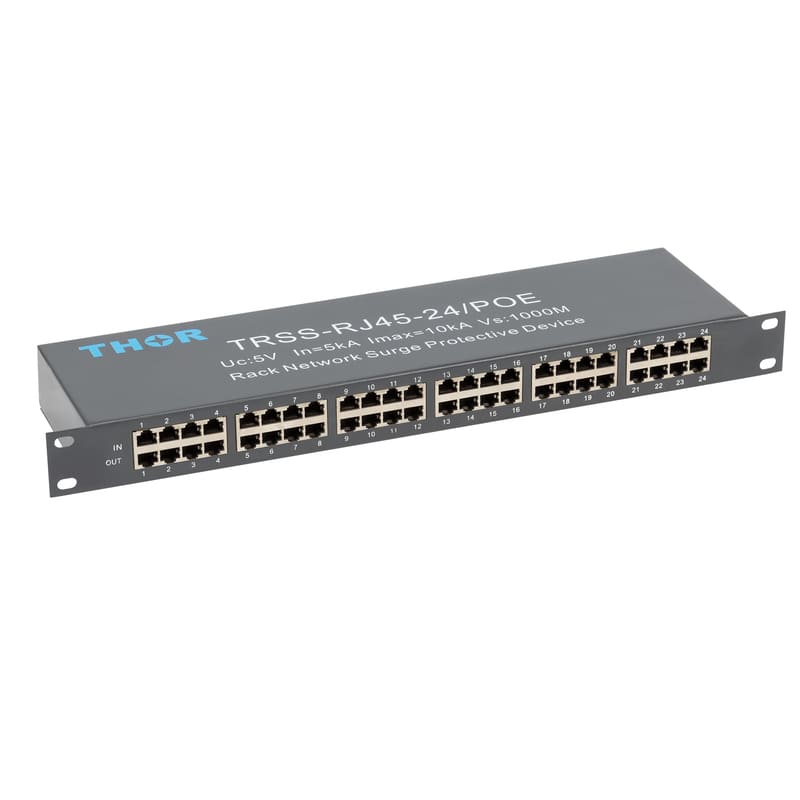
The electromagnetic pulse of lightning
There are four types of lightning: direct strike, induction (electromagnetic pulse), spherical thunder and cloud flash, with the first three being the most common. Direct lightning and spherical lightning will cause harm to people and buildings, and electromagnetic pulse mainly affects electronic equipment, mainly caused by induction.
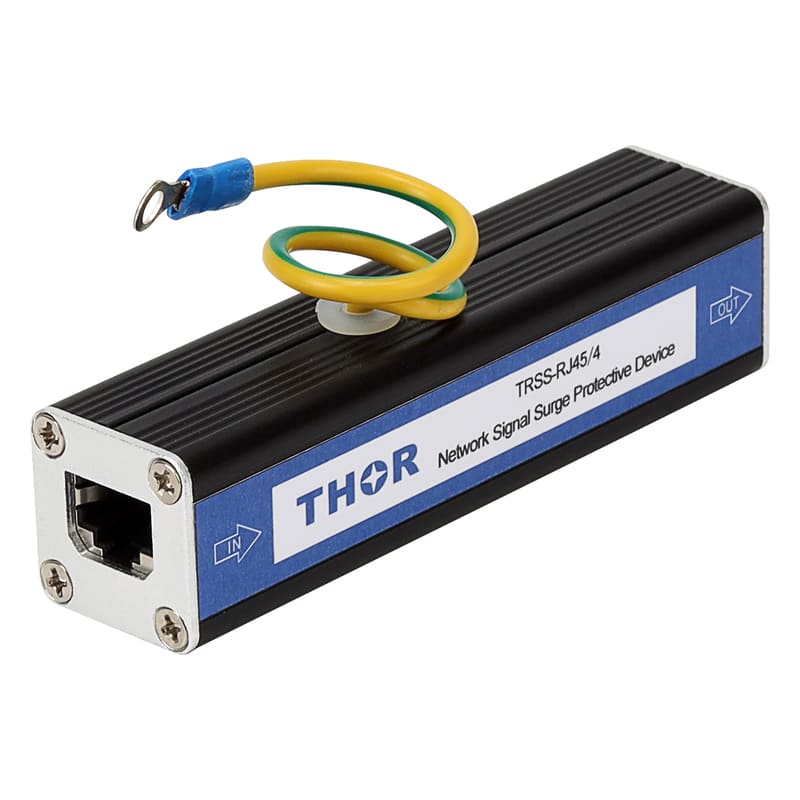
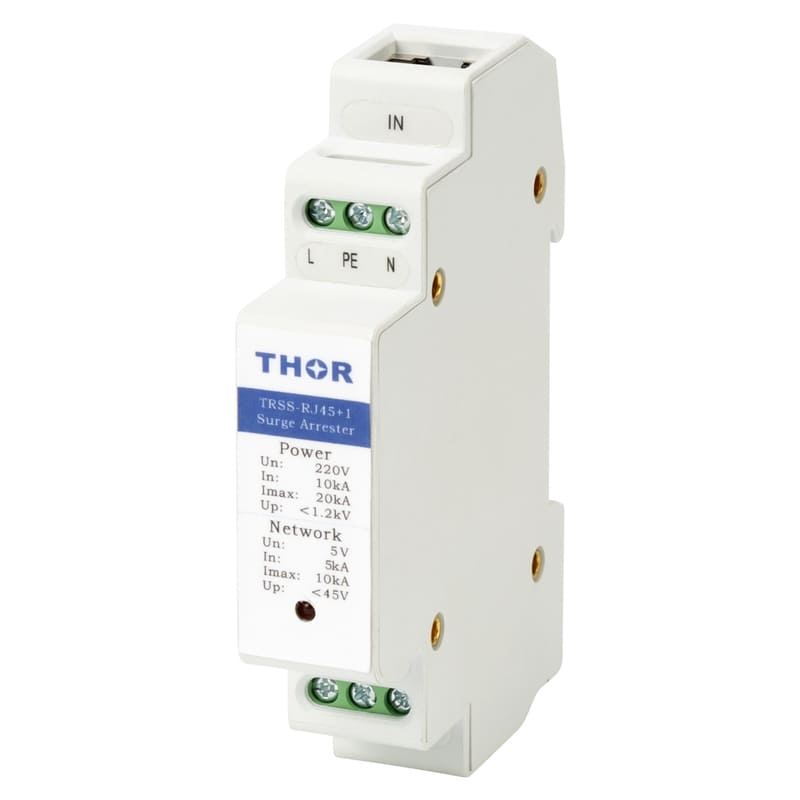
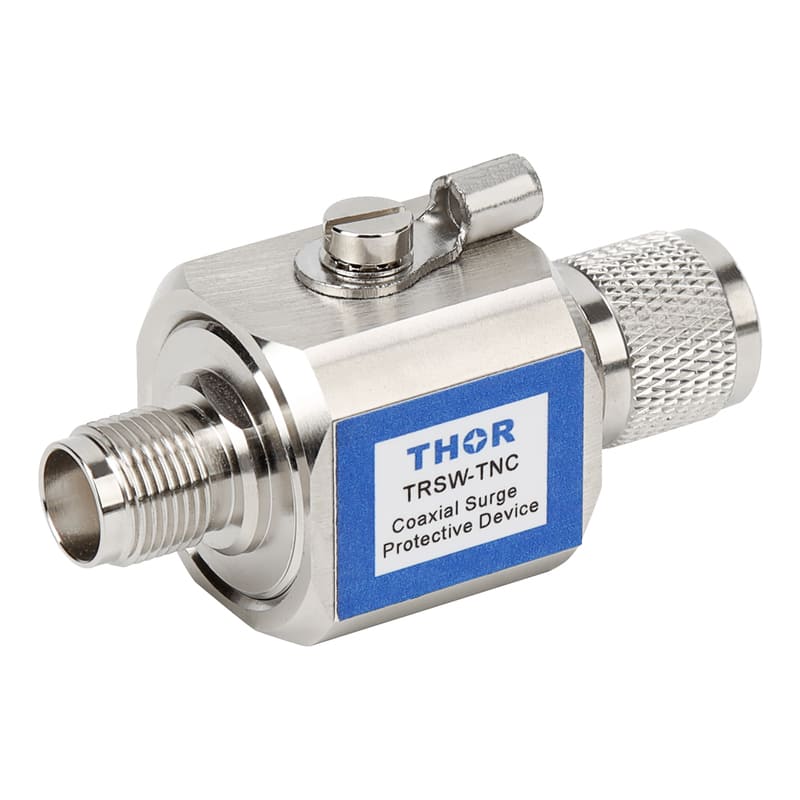
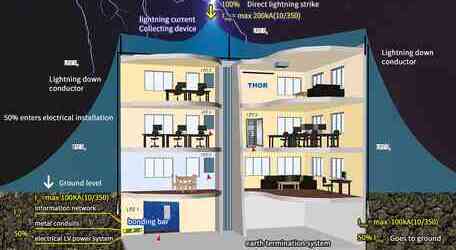
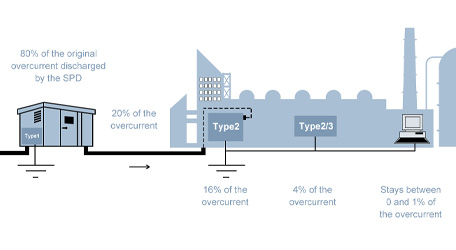
The electromagnetic pulse in lightning, therefore, is formed by the electrostatic induction of electrically charged clouds to a certain area of the ground with a heterogeneous charge. When the direct lightning occurs, the powerful pulse current to the surrounding wire or metal to produce electromagnetic induction of high voltage so as to occur the phenomenon of lightning, called "secondary lightning" or "induction thunder". The powerful transient electromagnetic field generated during lightning induction can generate induced charge in the ground metal network. Including wired and wireless communication networks, electric power transmission networks and other wire systems made of metal materials. The high intensity of the induced charge will form a strong transient high voltage electric field in these metal networks, which will form a high voltage arc discharge to the electrical equipment, and eventually cause the electrical equipment to burn. In particular, the damage to electronic and other weak current equipment is the most serious, such as TV, computer, communication equipment, office equipment and so on. Every year, inductive lightning damage electrical equipment accidents reach more than 10 million cases. This high voltage induction can also be harmful to people.
Therefore, the electromagnetic pulse protection method is basically the same as the lightning protection method